How Do QR Codes Work? A Simple Explanation
Ever wondered what happens when you scan a QR code? We break down the technology behind the black and white squares in a simple, easy-to-understand guide.
QR codes have become a part of our daily lives, but they can feel a bit like magic. You point your phone's camera at a strange-looking box of squares, and suddenly a website opens or you're connected to Wi-Fi. So, how does it actually work?
While the technology is clever, the basic concept is surprisingly simple. Let's break it down.
What Does 'QR' Stand For?
'QR' stands for Quick Response. They were invented in 1994 by a Japanese company called Denso Wave to track vehicle parts during manufacturing. They needed a code that could be scanned faster and hold more information than the standard barcodes of the day.
It's All About Storing Information
A QR code is simply a way of storing text information in a visual format. Your phone's camera reads this format and translates it back into text. This text can be anything:
- A website URL (e.g.,
https://qrfastgen.com) - Plain text (e.g., "This is a secret message")
- Wi-Fi network details (the network name and password)
- A vCard with contact information
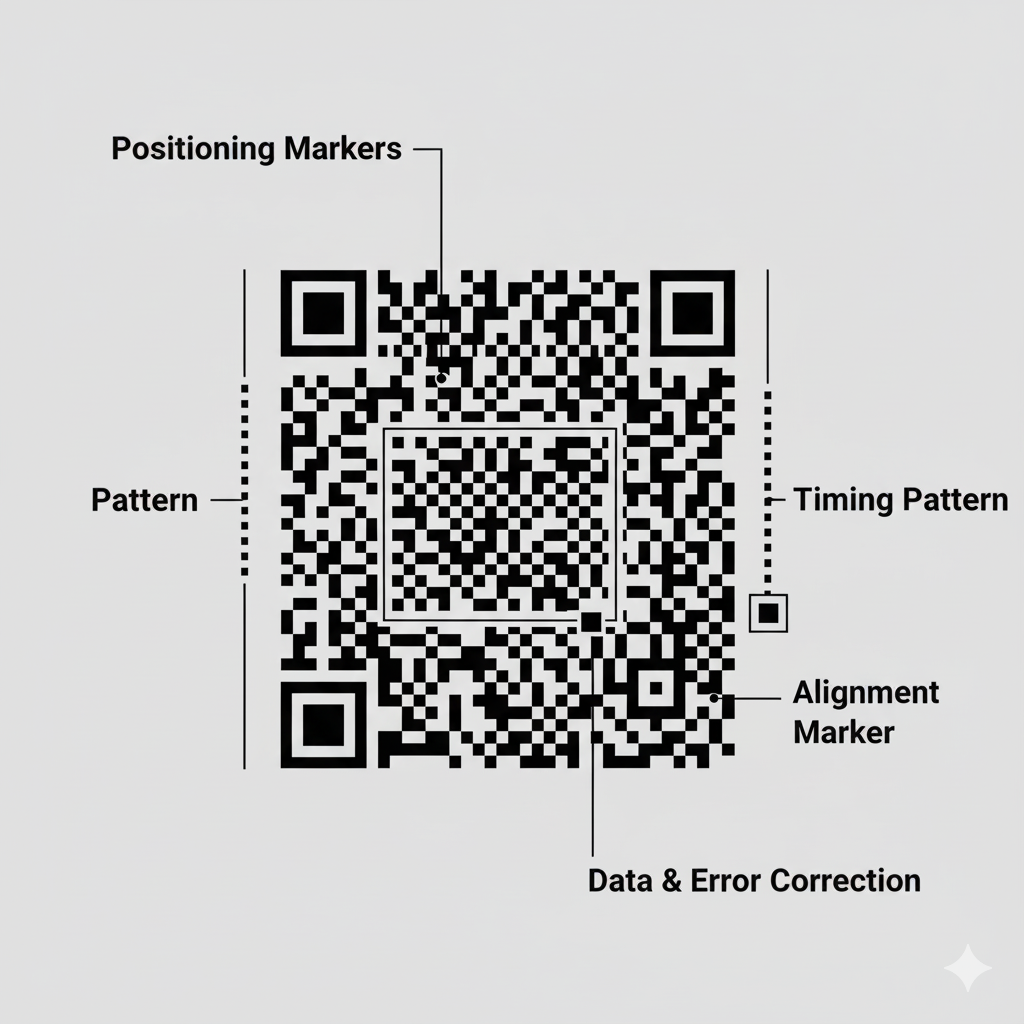
- Positioning Markers (The Big Squares): The three large squares in the corners are the most important part. They tell the scanner exactly where the QR code is and what its orientation is. This is why you can scan a QR code upside down and it still works!
- Alignment Marker (The Small Square): The smaller square, usually found near the bottom right, helps the scanner figure out the grid size and corrects for any distortion if the QR code is on a curved surface.
- Timing Pattern: The alternating black and white squares that run between the big positioning markers. This pattern helps the scanner determine the size of the individual modules (squares) in the code.
- The Data: All the other little squares in the code make up the actual information (the URL, text, etc.). This data also includes error correction information.
The Anatomy of a QR Code
A QR code isn't just a random jumble of squares. It has a specific structure that helps your phone read it quickly and accurately.
The Magic of Error Correction
Error correction is the secret weapon of QR codes. When a code is created, the data is stored redundantly. This means that even if a part of the QR code is damaged, dirty, or covered up (like when a brand puts its logo in the middle), the scanner can often still figure out the complete message by using the extra data to fill in the gaps.
This is why a QR code on a worn-out poster can still scan perfectly.
So, the next time you scan a QR code, you'll know exactly what's happening: your phone is using the corner markers to find the code, the timing patterns to understand the grid, and then reading the data squares to translate them back into the useful information you need. It's not magic—it's just very clever design!

About the Author
Amer Awadat
Amer is a software developer and tech enthusiast passionate about building useful tools that make technology accessible to everyone. As the creator of QRFastGen, he is focused on providing simple, powerful, and free solutions for the digital world.
Related Articles
Do QR Codes Expire? The Definitive Answer
A common question is whether QR codes expire. We break down the answer for both static and dynamic codes and explain what you need to know to ensure your code works forever.
Are QR Codes Safe? How to Spot and Avoid Malicious Codes
QR codes are convenient, but are they safe? Learn how to identify the risks, spot a malicious QR code, and protect yourself from scams.
5 Common QR Code Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
Is your QR code not scanning? Are you getting low engagement? You might be making one of these 5 common mistakes. Learn how to create effective QR codes every time.